Minimal downtime migrations
Minimal downtime migrations are only supported for MySQL and Postgres source databases.
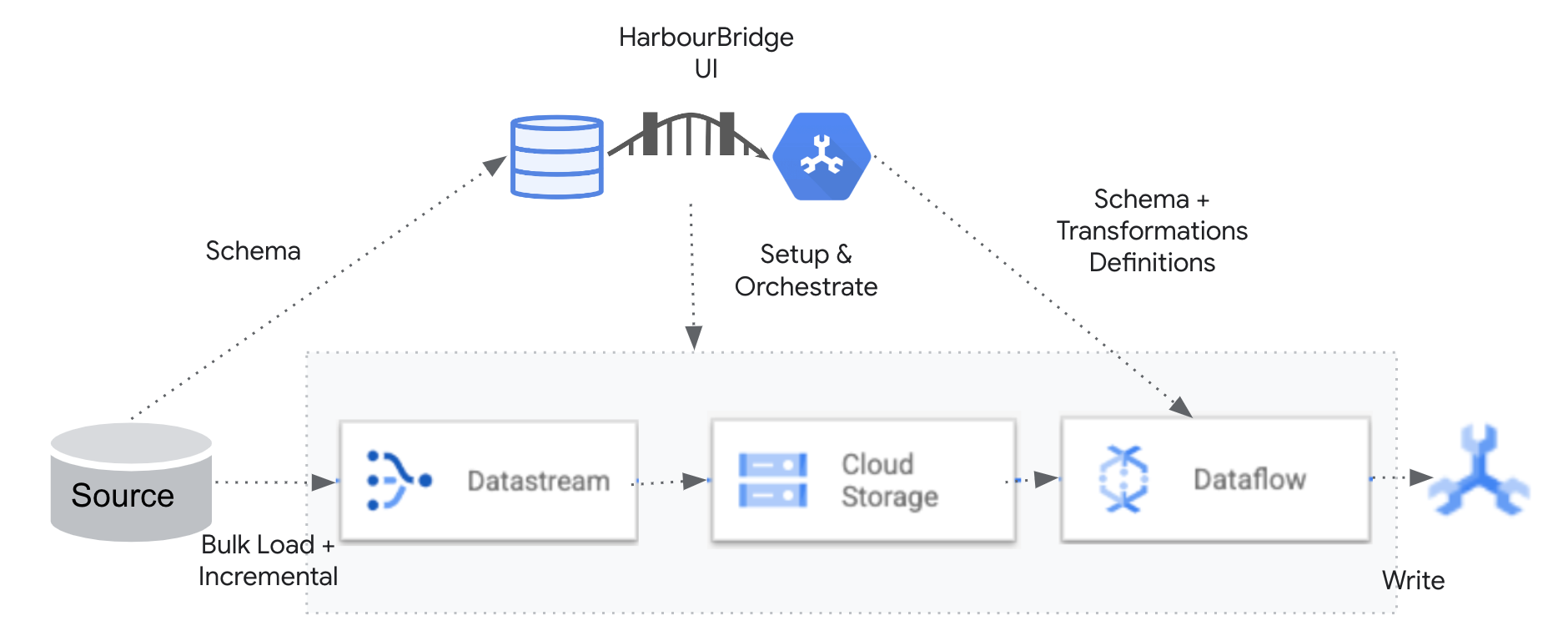
A minimal downtime migration consists of two components, migration of existing data from the database and the stream of changes (writes and updates) that are made to the source database during migration, referred to as change database capture (CDC). The process of migration involves Datastream reading data from the source database and writing to a GCS bucket, then GCS publishing a notification to Pub/Sub topic on each new file, then a Dataflow job when notified by the Pub/Sub subscription about the new file, reading the data from GCS bucket and writing to spanner database. With Spanner migration tool, this entire process can be orchestrated using a unified interface. Performing schema changes on the source database during the migration is not supported. This is the suggested mode of migration for most databases.
Sharded migrations
Sharded migrations are currently only supported for MySQL.
Spanner migration tool supports sharded migrations for MySQL. Spanner migration tool does this is by multiplexing a minimal downtime migration across multiple shards. It uses the user configured schema while transforming the data read from each shard, at the time of writing to Spanner automatically. This provides an integrated experience to perform an end-to-end sharded migration. Below is the architecture of how sharded migrations work:

Terminology
Due to the complex nature of sharded migrations, Spanner migration tool uses certain terminology to refer to different components of a sharded migration. Below is a brief description of each -
- Physical shard: A physical shard is an actual physical database instance with its unique IP endpoint. A physical shard can contain one more logical shard(s) in it. It is identified by a combination of four things - IP, User, Password and Port.
- Logical shard: A logical shard is a logical grouping of schema and data within a physical database instance. A physical database configuration + databaseName combination uniquely identifies a logical shard.
- Schema source: A schema source is a logical shard from which Spanner migration tool would read the schema for conversion. This needs to be explicitly defined by the user. Spanner migration tool does not migrate data from this shard (unless the schema source is also defined as a data shard – see below).
- Data shard: A data shard is a logical shard from which Spanner migration tool will read data for migration and write to Spanner. A schema source can also be a data shard. Spanner migration tool expects the schema inside a data shard to be identical to the schema in the schema source.
- Sharded database - A multi-endpoint, multi-shard (physical) setup, where each instance contains at-least one or more logical databases. Simply put, a sharded database is a set of physical shards (defined in [1] above). An instance is defined as a physical machine on which the source database is running.
- Streaming/Low Downtime/Minimal Downtime migration: A migration in which data is streamed from the source via Datastream and migrated onto Spanner via Dataflow. Spanner migration tool is used to perform schema conversions and orchestrate the required resources.